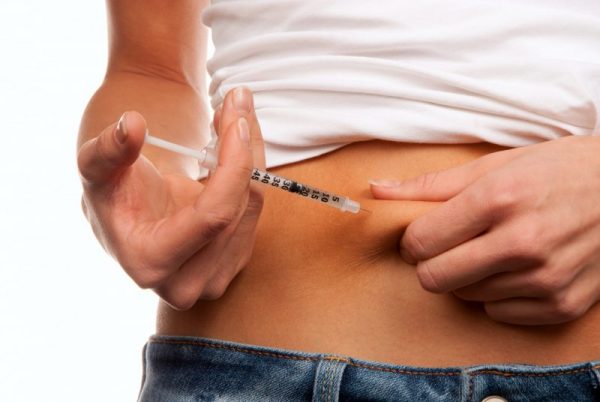
Semaglutide is a medication used to treat type 2 diabetes in adults and is being studied for its effectiveness as a weight loss aid. It is available in different dosages, and the recommended dosage depends on the patient’s needs.
Semaglutide is usually taken once a week as an injection, but there is also an oral formulation that is taken daily.
The starting dose of Semaglutide is usually 0.25 mg once a week for the first four weeks, followed by an increase to 0.5 mg once a week. After that, the dosage may be increased by 0.5 mg increments, up to a maximum dose of 2.4 mg once a week, depending on how the patient responds to the medication. The maximum dose in the clinical trial for Semaglutide’s use for weight loss (STEP program) was 2.4 mg once per week.
The oral formulation of Semaglutide is available in dosages of 3 mg and 7 mg, and it is typically taken once a day with or without food.
Patients should follow their doctor’s instructions regarding the dosage and timing of Semaglutide administration. It is important to not change the dosage without consulting a healthcare professional.
If a patient misses a dose of Semaglutide, they should take it as soon as they remember. However, if it is close to the time for their next dose, they should skip the missed dose and continue with their regular dosing schedule.
Overdose of Semaglutide can lead to serious side effects, including hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and pancreatitis. It is important to seek medical attention immediately if an overdose is suspected.